Software Engineer
What is AI ?
History Of AI

The term AI is coined at the Dartmouth Conference.
1956The Dartmouth Conference, held in the summer of 1956, is considered the founding event of artificial intelligence as a field. Organized by John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon, it was the first use of the term "artificial intelligence".
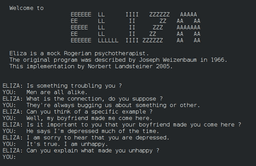
ELIZA, the first chatbot, is created.
1966Joseph Weizenbaum created ELIZA, a computer program that can simulate a conversation with a human. It was an early example of natural language processing (NLP).

IBM's Deep Blue defeats world chess champion Garry Kasparov.
1997In 1997, IBM's chess-playing computer, Deep Blue, defeated world champion Garry Kasparov in a six-game match. This was a significant milestone in AI development.

IBM Watson wins Jeopardy! against former champions.
2011IBM Watson, a question-answering computer system, competed on the quiz show Jeopardy! and defeated two of the game's greatest champions, Ken Jennings and Brad Rutter.

Google DeepMind's AlphaGo defeats professional Go player.
2014In 2014, Google DeepMind's AlphaGo became the first AI program to defeat a professional human player at the game of Go. It later defeated world champion Lee Sedol in 2016.

OpenAI's GPT-3 is released.
2020OpenAI released GPT-3, a state-of-the-art language processing AI model that can generate human-like text based on the input it receives. It has 175 billion parameters.

OpenAI releases GPT-4.
2023OpenAI released GPT-4, an even more advanced version of its predecessor, with significant improvements in understanding and generating human language.
Why Use AI?
Fast
AI can write and fix code quickly.
Saving Time
With AI we can save time in the development process.
Troubleshoot
AI can detect and identify problems quickly through log data analysis and real-time system monitoring.
SEO Optimization
AI improves content for better SEO performance.
Security
AI can detect and identify security vulnerabilities quickly through log data analysis and real-time system monitoring.
Data Analysis
AI can analyze data quickly through log data analysis and real-time system monitoring.